Ten Signs That Indicate You Have A Magnesium Deficiency

Magnesium is an essential mineral that is abundantly present in the human body, playing a role in over 300 physiological processes. Regrettably, magnesium deficiency is pervasive in our society today.
Could this deficiency be negatively affecting your health? This article delves into the indicators of magnesium deficiency and suggests effective ways to incorporate more magnesium into your diet
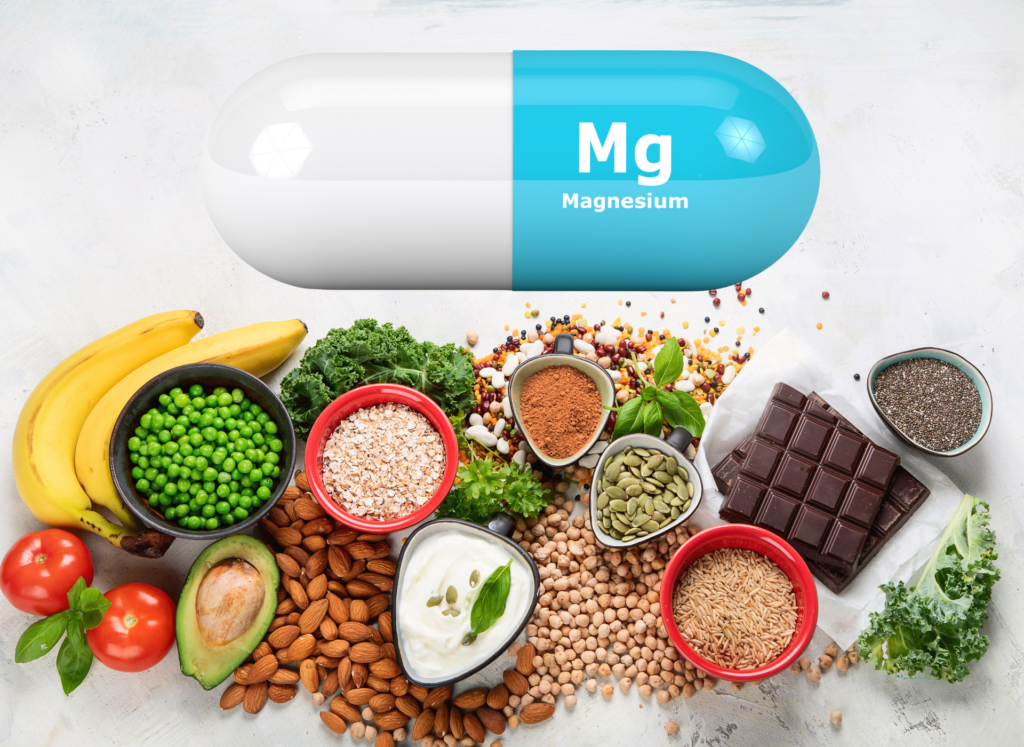

According to American neurosurgeon Norman Shealy, MD, PhD, nearly every known disease is associated with a magnesium deficiency.

While this might seem like a bold assertion, it aligns with magnesium’s multifaceted roles in the body. This diversity of functions explains the wide array of symptoms that manifest when magnesium levels are insufficient.

1. Impaired Cognitive Function
Experiencing frequent brain fog, poor concentration, or persistent memory problems could indicate a magnesium deficiency. Mitochondria, cellular structures responsible for energy production, particularly in the brain, heavily rely on magnesium.
Thus, a deficiency can significantly hamper cognitive performance. It’s worth noting that supplementing with magnesium has been shown to enhance learning and memory.

2. Headaches and Migraines
Research suggests that individuals suffering from chronic migraines often have lower magnesium levels. Magnesium’s role in regulating nerve function and neurotransmitter production makes this association understandable.
Regular magnesium supplementation has been found to reduce both the frequency and intensity of migraine headaches, even benefiting non-migraine headaches.

This effect stems from magnesium’s ability to regulate calcium balance in neuronal cells, preventing overstimulation, a major factor in headache and migraine development.

3. Constipation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
If you frequently experience constipation, magnesium deficiency might be a contributing factor.
Adequate magnesium intake helps soften stools by drawing water into the bowels, promoting healthy elimination.
Magnesium also regulates muscle contractions in the intestines, making it valuable for relieving discomfort and cramping related to conditions like IBS.

4. Persistent Fatigue
Magnesium plays a pivotal role in energy production. Mitochondria, reliant on magnesium for energy generation, significantly influence your energy levels. Moreover, magnesium supports adrenal gland function, another key player in energy production.
A magnesium deficiency can hinder over 300 normal bodily processes, placing chronic stress on your system and sapping your energy. If you experience chronic fatigue, consider boosting your magnesium intake to enhance your energy levels.

5. Insomnia
Many individuals find relief from insomnia through magnesium supplementation. Magnesium is involved in the production of GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation. Insufficient magnesium can lead to poor sleep quality, making it a potential contributor to insomnia.

6. Muscle Spasms and Cramps
Due to its importance in nerve transmission, magnesium deficiency often leads to muscle weakness and uncoordinated contractions, resulting in spasms and painful cramps. These spasms commonly affect the legs, feet, and even eyelids. Women may also experience worsened PMS-related cramping when magnesium levels are low.

7. Chronic Pain and Fibromyalgia
Chronic pain and conditions like fibromyalgia are linked to physical tension in the body. Emotional stress exacerbates this tension, leading to pain over time. Low magnesium levels can make the nervous system hyperexcitable, increasing muscle tension. Magnesium can help by inducing an overall calming effect on the mind and body while relaxing muscles.

8. Heart Arrhythmia
The heart, a muscle that constantly contracts, relies heavily on magnesium for proper functioning. Magnesium regulates calcium and potassium concentrations in cardiac muscle tissue, which is crucial for maintaining a steady heartbeat. Irregular heart rhythms, including rapid or slow beats, can be a sign of magnesium deficiency.

9. Numbness and Tingling
Frequent numbness or tingling sensations, often in the hands and feet, may be related to changes in nerve activity. While limited research has been conducted on this specific mechanism, magnesium deficiency might play a role.
Some studies suggest that magnesium could alleviate or prevent numbness and tingling, particularly in the extremities.
10. Mood Disorders
Magnesium plays a vital role in regulating neurotransmitter balance in the brain. It is particularly involved in the production of GABA, a calming neurotransmitter.
Inadequate GABA production can lead to conditions like ADD/ADHD, anxiety, irritability, and mood imbalances. If you regularly experience these feelings, increasing your daily magnesium intake may be beneficial.
Ways to Support Magnesium Levels
Now that you are aware of the signs of magnesium deficiency and its significance for the body, it’s crucial to know how to increase your magnesium intake. Here are three strategies to boost your magnesium levels and enhance your health:
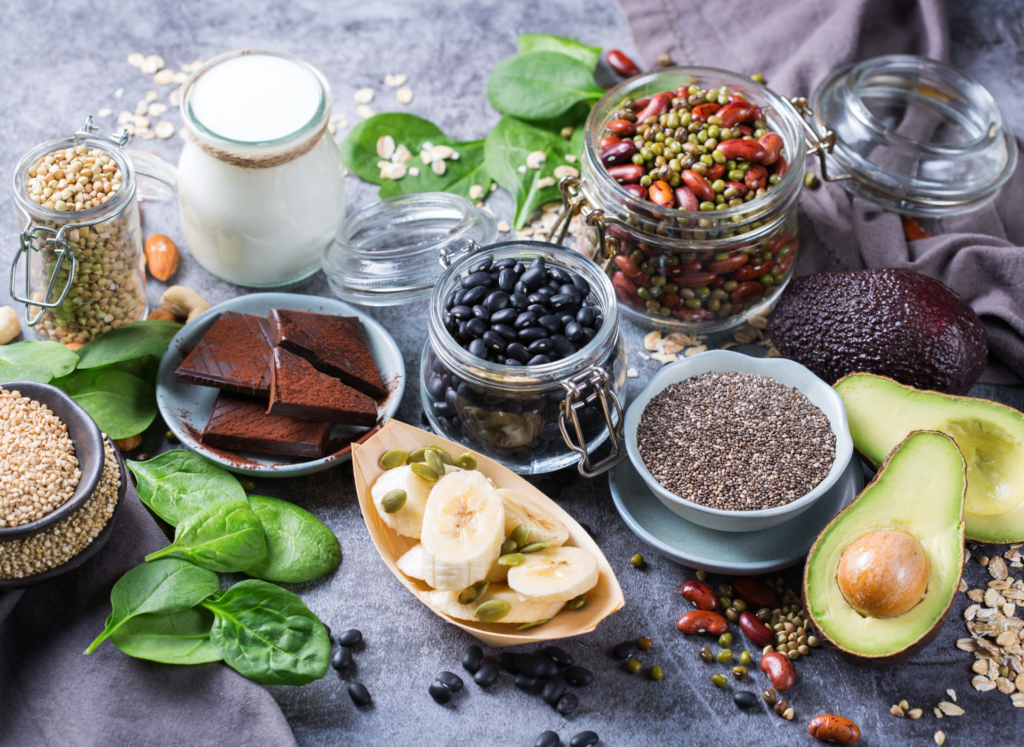

1. Magnesium-Rich Foods
Begin by adjusting your diet to include magnesium-rich foods. Some excellent sources include avocados, leafy green vegetables, and dark chocolate.
Incorporate these foods into your daily meals to ensure an adequate magnesium intake. Consider exploring recipes that feature magnesium-rich ingredients to make it enjoyable.

2. Epsom Salt Baths
Relax and replenish magnesium through Epsom salt baths. Epsom salts contain magnesium, which can be absorbed through the skin during a bath, promoting relaxation.
You can choose between traditional Epsom salts made of magnesium sulfate or newer forms like magnesium chloride for potentially longer-lasting benefits.

3. Dietary Supplements
Due to modern agricultural practices depleting soil nutrients, dietary sources alone may not suffice. Consider supplementing your diet with magnesium. Opt for high-quality transdermal magnesium or powdered forms.
Transdermal magnesium, available in lotion form, can be applied to the skin for quick absorption, bypassing potential digestive issues.
In conclusion, magnesium is a crucial mineral for overall well-being. Even if you don’t exhibit the common symptoms of magnesium deficiency, incorporating more magnesium into your diet can be advantageous. Many individuals, including health-conscious individuals, find daily magnesium supplementation beneficial, as it supports mental calmness, balanced energy levels, and resilience to everyday stressors.
Menu
